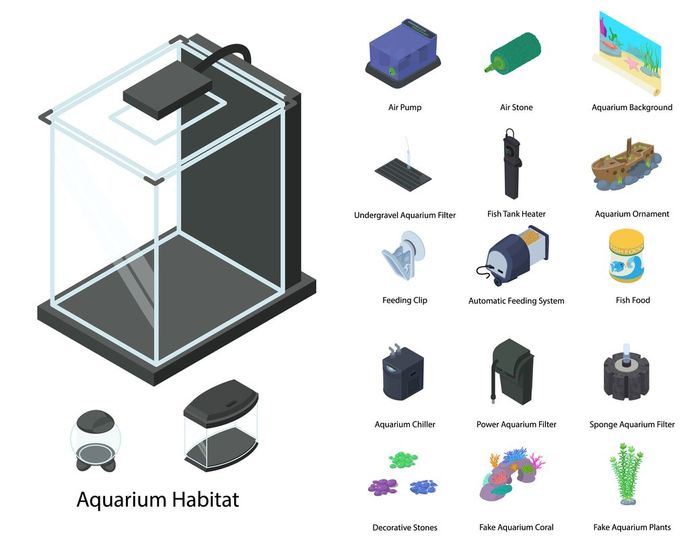
Happy Healthy Fish!
Whether designing a freshwater planted aquarium, a paludarium, a saltwater fish only aquarium, or a one of a kind saltwater reef aquarium, we have all the answers and experience to meet and exceed all of your expectations. To ensure your aquatic friends stay healthy, it is essential to keep the conditions of your tank optimal. Filters help maintain the tank but if not maintained the filter can become clogged and cause more harm than good. Fish continuously produce waste, the food they do not eat decays, and potentially harmful byproducts slowly build up endangering your fish’s life. Fish tanks requires routine maintenance and cleaning to help sustain the delicate ecosystem in your tank.
What's in your Aquarium?
pH levels and your aquatic family
PH is the measure of how acidic or basic a solution is.
Usually, you do not need to worry about pH levels unless your pH levels are dangerously high or low. Most fish can live in a wide array of pH levels.
If you have elevated levels of ammonia in your aquarium. it will be more toxic if the pH is higher.
Filling from the tap
Water from the tap has chlorine or chloramine added to make it safe to drink for us humans. But sadly these are poisonous to our fishy friends.
Any time tap water is added to the aquarium, a water conditioner must be used to remove any chlorine/chloramine that is present.
Oh No-Ammonia
Ammonia (NH3) is poisonous to fish. It is expelled through the gill membranes of our aquatic friends, introducing nitrogen into the aquarium.
But don’t worry eventually, Ammonia will be converted into nitrite by “good” bacteria.
Nitrite and Nitrate
Nitrite (N02) is also poisonous to fish. It results from some non-fish waste breakdown, i.e. uneaten fish food, and normal ammonia oxidation by "good" bacteria.
Nitrate (N03) is not as poisonous, but high concentrations for lengthy periods of time can injure fish. It is the result of natural nitrite oxidation by "good" bacteria.
What is General Hardness (GH)?
GH is the amount of calcium and magnesium ions in the water. A low GH level is referred to as soft water, a high GH level is known as hard water.
Most fish can dwell in a wide range of GH levels, but some fish types may be more sensitive to changes in GH.
KH, Carbonate Hardness, and Alkalinity
KH, carbonate hardness, is the amount of carbonates and bicarbonates in the water.
Proper KH levels are important to help to stabilize pH levels within the aquarium.
With regularly scheduled partial water changes using tap water. KH will typically remain at a good level.
Is it hot or is it cold?
Normal range for tanks are between 74 to 82 degrees Fahrenheit. (23 to 28 C). it is very important it stays the same because sudden changes in temperature can harm fish. Best practice is to use an aquarium heater to keep a consistent temperature.